Multicollinearity
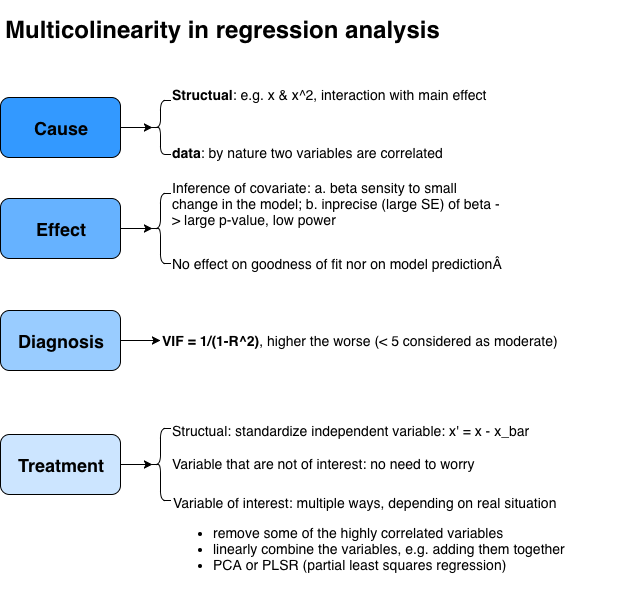
Cause
- Structural: e.g. $x \ \&\ x^2$, interaction term and the main effect included in the interaction term
- Data: by nature two variables are correlatd
Eeffect
- Inference of covariate
- $\beta$ becomes sensitive to small change in the model
- imprecise (i.e. large s.e.) of $\beta\rightarrow$ large p-value, low power
- NO effect on goodness-of-fit nor on model prediction
Diagnosis
-
VIF: variance inflation factor of variable $x_i$, higher the worse (usually < 5 is moderate), is defined as:
$$\text{VIF}_i = \frac{1}{1-R_i^2}$$where $R_i^2$ is the coefficient of determination when regression $X_i$ on the rest of the indepdent variables.
Treatment
- Structural: standardize indepndent variable, e.g. $X' = X - \bar{X}$
- Variables that are not of interest: no need to worry
- Variables that are of interest:
- remove some of the highly correlated variables
- Linearly combine the variables, e.g. adding them together
- PCA or PLSR (partial least squares regression, ?)